Interpretation of Industry Standard YS/T 888-2024
Release time:2025-10-10
Interpretation of Industry Standard YS/T 888-2024 "Technical Specification for Recycling Waste Wires and Cables"
I. Background and Significance of the Standard's Development
In recent years, China's non-ferrous metal recycling industry has continuously expanded, with steady industry development. Data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) shows that the total amount of recycled renewable resources exceeds 280 million tons, with recycled scrap steel being the highest, exceeding 220 million tons. The recycling volume of the four major non-ferrous metals (copper, aluminum, lead, zinc) exceeds 12 million tons. The sustained development of the renewable resources industry provides a strong guarantee for optimizing industrial structure, reducing environmental pollution, and conserving national resources in China's non-ferrous metals, ferrous metals, and plastics industries. Recycled copper, aluminum, steel, and polymer materials obtained from the disassembly of waste wires and cables are effective and reliable sources of these renewable resources.
Optimizing the recycling, trading, processing, and utilization processes of renewable resources like waste wires and cables is particularly important, both from the perspective of fully utilizing renewable resources and protecting the environment. The "Technical Specification for Recycling Waste Wires and Cables" industry standard plays a guiding role in the recycling and disassembly of waste wires and cables, providing an important reference for related enterprises in the non-ferrous metals, ferrous metals, and polymer industries involved in recycling, disassembly, trading, processing, and reuse.
The current waste wire and cable recycling system faces the following problems: Firstly, recycling channels are decentralized, mostly dominated by individual businesses, with few large-scale enterprises, making unified recycling and processing difficult. Secondly, the disassembly process is mostly manual, with low levels of mechanization and automation, resulting in high labor intensity for workers. Thirdly, the specialization level of operational workers is low, with weak awareness of classifying various resources, affecting the recovery rate of renewable resources. Fourthly, there is a lack of specific operational standards for reference, and the recycling and disassembly system has not formed a standardized and normalized framework.
Therefore, the original YS/T 888-2013 "Classification of Waste Wires and Cables" standard could no longer meet the current requirements of waste wire and cable recycling enterprises and various renewable resource recycling and reuse entities, necessitating the revision of this standard to meet the needs of relevant industries and units involved with waste wires and cables.
II. Main Development Process
According to the "Notice of the General Office of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on Issuing the 2021 Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality Special Industry Standard Formulation and Revision Project Plan" (MIIT Office Letter [2021] No. 291), the task of revising the "Classification of Waste Wires and Cables" industry standard (project plan number: 2021-1761T-YS) was assigned. After the plan was issued, the drafting team held multiple meetings to finalize tasks and conduct preliminary reviews. Through discussions and revisions by participating experts, a draft for comments was formed and published online for soliciting opinions. The technical expert review was completed in February 2023, and the standard passed the review by all members of the Heavy Metals Sub-Technical Committee of the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Nonferrous Metals in April 2023. The standard was submitted for approval in June 2023, released on March 29, 2024, and will be officially implemented on October 1, 2024.
III. Main Content of the Standard
3.1 Scope of Application
To meet the needs of standardizing the recycling of waste wires and cables, the revision of YS/T 888-2013 "Classification of Waste Wires and Cables" changed the standard's function from a classification standard to a process specification standard.
3.2 General Requirements
This standard is a process specification standard, stipulating the general requirements for enterprises recycling waste wires and cables, including four main aspects: general requirements, equipment requirements, site requirements, and safety requirements. By combining the actual situation of enterprises during recycling activities and the requirements of national laws and regulations, and referencing multiple national and industry standards in the field of waste resource recycling, the following specific contents are mainly proposed:
3.2.1 Regarding the general requirements for recycling enterprises, detailed explanations are provided for relevant qualifications, principles to follow, management systems, recycling methods, classified management and disposal of various solid waste properties, etc.
3.2.2 Regarding equipment configuration requirements, specific regulations are proposed for necessary production process mechanization, necessary public auxiliary facilities, necessary environmental protection equipment, and equipment safety devices, which can improve the efficiency of waste wire and cable recycling work and promote industry progress.
3.2.3 Regarding recycling site requirements, normative requirements are proposed for site selection, safety protection facilities, vibration prevention, ground hardening, area, etc., to ensure the standardization and suitability of the site.
3.2.4 Regarding safety requirements, detailed requirements are proposed for the basic safety and operational safety of workers, which can improve the safety of enterprises engaged in waste wire and cable recycling operations.
3.3 Technical Requirements
3.3.1 Recycling Process Flow
This standard defines the recycling process flow for waste wires and cables, mainly including manual sorting, preliminary mechanical disassembly, pretreatment, mechanical disassembly, mechanical sorting, and comprehensive recycling. The specific process is shown in Figure 1.

3.3.2 Manual Sorting
Regarding the removal of large pieces of free iron that affect production safety and equipment lifespan, stones that affect material recovery rates, and other substances outside the main body of the waste wires and cables, there are no mature direct mechanized processing equipment in the industry yet. Currently, these substances can only be removed through manual sorting. Simultaneously during sorting, waste wires and cables should be classified according to Table 1.
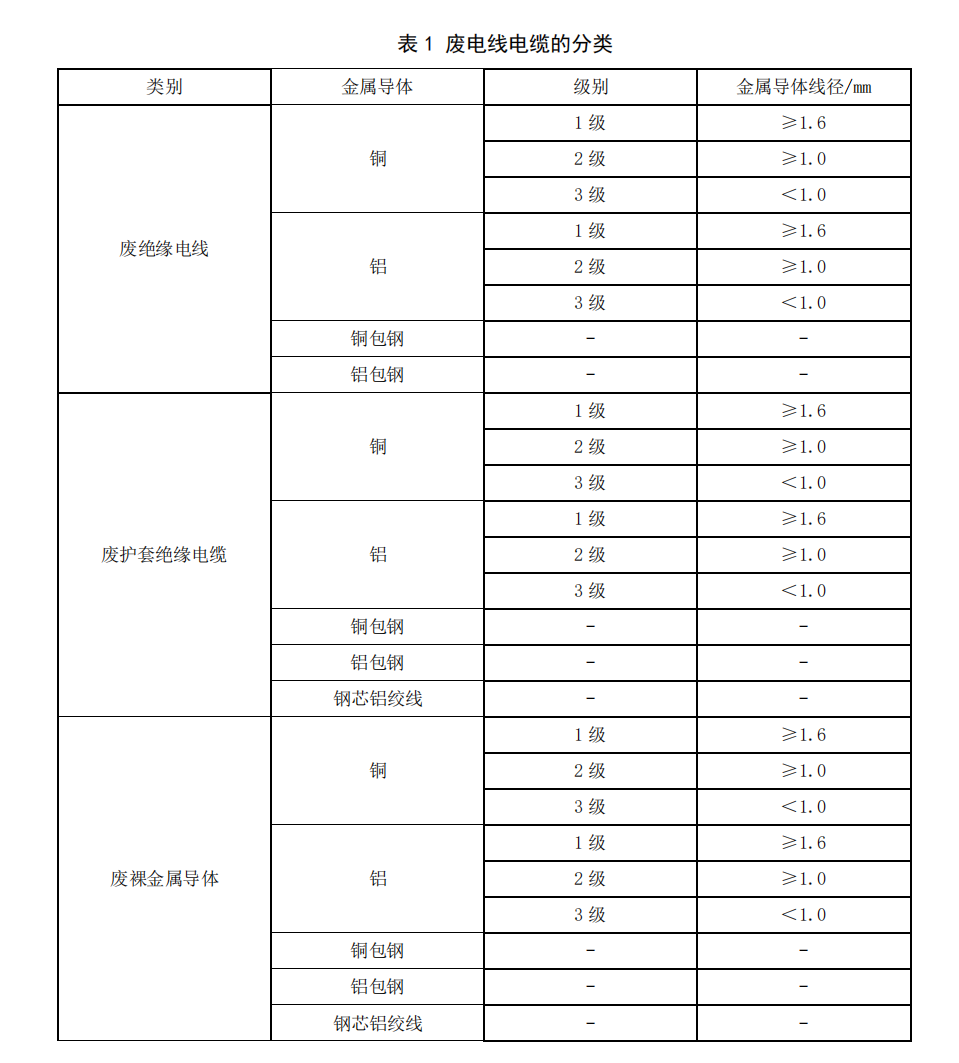
The "Main Content" indicator should be set within the functional type of a "product standard," used by trading parties as a basis for grading and transaction pricing. After this revision, as a process specification standard, it should not require the "Main Content" of the metal conductor in the incoming "waste wires and cables"; the focus is on the normative requirements of the recycling process. Therefore, mentioning the "Main Content" indicator is unnecessary.
3.3.3 Preliminary Mechanical Disassembly
Added normative requirements for preliminary mechanical disassembly, proposing the use of stripping equipment for this purpose; proposed treatment methods for waste sheathed and insulated cables after stripping.
3.3.4 Pretreatment
Added normative requirements for pretreatment, proposing the use of shredders or guillotine shears for pretreatment; proposed suggested specific sizes for waste wires and cables after pretreatment.
3.3.5 Mechanical Disassembly
Added normative requirements for mechanical disassembly, proposing the use of crushers for mechanical disassembly.
3.3.6 Mechanical Sorting
Added normative requirements for mechanical sorting, proposing the use of equipment such as gravity separators, magnetic separators, flotation separators, air separators, or screening machines for mechanical sorting.
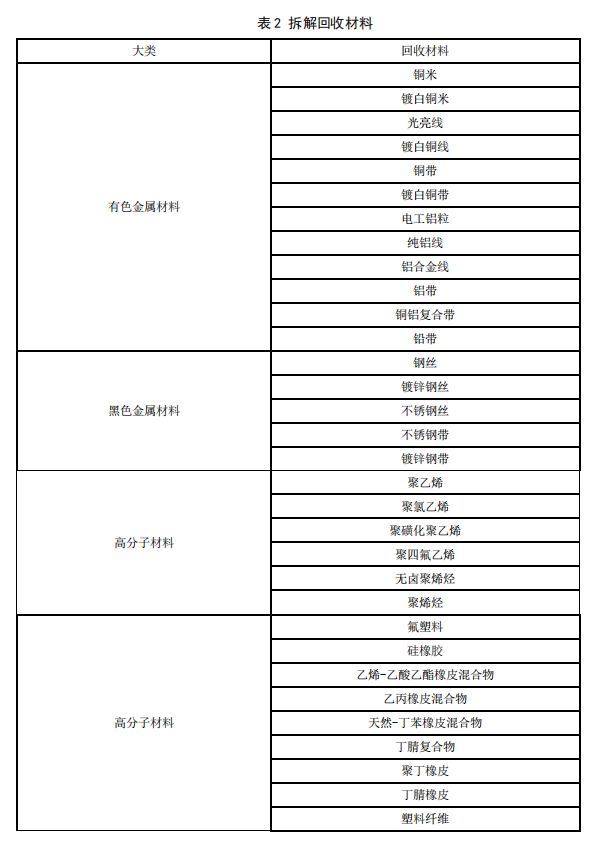
3.3.7 Comprehensive Recycling and Disassembled/Recycled Materials
3.4 Environmental Protection Requirements
This standard proposes specific normative requirements for wastewater, solid waste, exhaust gases, and noise generated during the enterprise's recycling process.
IV. Significance of Standard Implementation
According to data, China produced approximately 8.1 million tons of copper-based waste wires and cables and about 2 million tons of aluminum conductor-based waste wires and cables in 2021. Based on estimates, recycling and disassembling the aforementioned waste wires and cables could recover approximately 1.35 million tons of copper, 200,000 tons of aluminum, 1 million tons of steel, and about 7 million tons of polymer materials. While standardizing the recycling practices for waste wires and cables, this standard, by combining multiple sorting technologies and multi-stage sorting, ensures the maximization of renewable resource utilization, reducing the high mixing ratio of renewable resources caused by incomplete sorting, which adds unnecessary energy consumption for the users of these renewable resources, thereby contributing to China's energy conservation and emission reduction efforts. Furthermore, when enterprises conduct waste wire and cable recycling activities according to the requirements proposed in this standard, they have corresponding normative directions for rectifying the "three wastes" (waste water, gas, solid waste) and noise generated during the process. Building green and friendly enterprises can contribute to China's green environmental protection cause.
In summary, the revision of this standard has the following significant meanings: 1) It can improve the technical level of waste wire and cable recycling enterprises and reduce the industry's environmental pollution; 2) It further enhances the level of mechanization and automation of recycling operations, improving production efficiency and safety; 3) It promotes the development of enterprises towards larger scales, enhances the competitiveness of recycling enterprises, and encourages the healthy development of the industry; 4) It improves the efficiency of recycling and reusing various renewable resources, contributing to the national cause of renewable resource utilization.
Contact Information
I. Background and Significance of the Standard's Development
In recent years, China's non-ferrous metal recycling industry has continuously expanded, with steady industry development. Data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) shows that the total amount of recycled renewable resources exceeds 280 million tons, with recycled scrap steel being the highest, exceeding 220 million tons. The recycling volume of the four major non-ferrous metals (copper, aluminum, lead, zinc) exceeds 12 million tons. The sustained development of the renewable resources industry provides a strong guarantee for optimizing industrial structure, reducing environmental pollution, and conserving national resources in China's non-ferrous metals, ferrous metals, and plastics industries. Recycled copper, aluminum, steel, and polymer materials obtained from the disassembly of waste wires and cables are effective and reliable sources of these renewable resources.
Optimizing the recycling, trading, processing, and utilization processes of renewable resources like waste wires and cables is particularly important, both from the perspective of fully utilizing renewable resources and protecting the environment. The "Technical Specification for Recycling Waste Wires and Cables" industry standard plays a guiding role in the recycling and disassembly of waste wires and cables, providing an important reference for related enterprises in the non-ferrous metals, ferrous metals, and polymer industries involved in recycling, disassembly, trading, processing, and reuse.
The current waste wire and cable recycling system faces the following problems: Firstly, recycling channels are decentralized, mostly dominated by individual businesses, with few large-scale enterprises, making unified recycling and processing difficult. Secondly, the disassembly process is mostly manual, with low levels of mechanization and automation, resulting in high labor intensity for workers. Thirdly, the specialization level of operational workers is low, with weak awareness of classifying various resources, affecting the recovery rate of renewable resources. Fourthly, there is a lack of specific operational standards for reference, and the recycling and disassembly system has not formed a standardized and normalized framework.
Therefore, the original YS/T 888-2013 "Classification of Waste Wires and Cables" standard could no longer meet the current requirements of waste wire and cable recycling enterprises and various renewable resource recycling and reuse entities, necessitating the revision of this standard to meet the needs of relevant industries and units involved with waste wires and cables.
II. Main Development Process
According to the "Notice of the General Office of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on Issuing the 2021 Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality Special Industry Standard Formulation and Revision Project Plan" (MIIT Office Letter [2021] No. 291), the task of revising the "Classification of Waste Wires and Cables" industry standard (project plan number: 2021-1761T-YS) was assigned. After the plan was issued, the drafting team held multiple meetings to finalize tasks and conduct preliminary reviews. Through discussions and revisions by participating experts, a draft for comments was formed and published online for soliciting opinions. The technical expert review was completed in February 2023, and the standard passed the review by all members of the Heavy Metals Sub-Technical Committee of the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Nonferrous Metals in April 2023. The standard was submitted for approval in June 2023, released on March 29, 2024, and will be officially implemented on October 1, 2024.
III. Main Content of the Standard
3.1 Scope of Application
To meet the needs of standardizing the recycling of waste wires and cables, the revision of YS/T 888-2013 "Classification of Waste Wires and Cables" changed the standard's function from a classification standard to a process specification standard.
3.2 General Requirements
This standard is a process specification standard, stipulating the general requirements for enterprises recycling waste wires and cables, including four main aspects: general requirements, equipment requirements, site requirements, and safety requirements. By combining the actual situation of enterprises during recycling activities and the requirements of national laws and regulations, and referencing multiple national and industry standards in the field of waste resource recycling, the following specific contents are mainly proposed:
3.2.1 Regarding the general requirements for recycling enterprises, detailed explanations are provided for relevant qualifications, principles to follow, management systems, recycling methods, classified management and disposal of various solid waste properties, etc.
3.2.2 Regarding equipment configuration requirements, specific regulations are proposed for necessary production process mechanization, necessary public auxiliary facilities, necessary environmental protection equipment, and equipment safety devices, which can improve the efficiency of waste wire and cable recycling work and promote industry progress.
3.2.3 Regarding recycling site requirements, normative requirements are proposed for site selection, safety protection facilities, vibration prevention, ground hardening, area, etc., to ensure the standardization and suitability of the site.
3.2.4 Regarding safety requirements, detailed requirements are proposed for the basic safety and operational safety of workers, which can improve the safety of enterprises engaged in waste wire and cable recycling operations.
3.3 Technical Requirements
3.3.1 Recycling Process Flow
This standard defines the recycling process flow for waste wires and cables, mainly including manual sorting, preliminary mechanical disassembly, pretreatment, mechanical disassembly, mechanical sorting, and comprehensive recycling. The specific process is shown in Figure 1.

3.3.2 Manual Sorting
Regarding the removal of large pieces of free iron that affect production safety and equipment lifespan, stones that affect material recovery rates, and other substances outside the main body of the waste wires and cables, there are no mature direct mechanized processing equipment in the industry yet. Currently, these substances can only be removed through manual sorting. Simultaneously during sorting, waste wires and cables should be classified according to Table 1.

The "Main Content" indicator should be set within the functional type of a "product standard," used by trading parties as a basis for grading and transaction pricing. After this revision, as a process specification standard, it should not require the "Main Content" of the metal conductor in the incoming "waste wires and cables"; the focus is on the normative requirements of the recycling process. Therefore, mentioning the "Main Content" indicator is unnecessary.
3.3.3 Preliminary Mechanical Disassembly
Added normative requirements for preliminary mechanical disassembly, proposing the use of stripping equipment for this purpose; proposed treatment methods for waste sheathed and insulated cables after stripping.
3.3.4 Pretreatment
Added normative requirements for pretreatment, proposing the use of shredders or guillotine shears for pretreatment; proposed suggested specific sizes for waste wires and cables after pretreatment.
3.3.5 Mechanical Disassembly
Added normative requirements for mechanical disassembly, proposing the use of crushers for mechanical disassembly.
3.3.6 Mechanical Sorting
Added normative requirements for mechanical sorting, proposing the use of equipment such as gravity separators, magnetic separators, flotation separators, air separators, or screening machines for mechanical sorting.
3.3.7 Comprehensive Recycling and Disassembled/Recycled Materials

3.4 Environmental Protection Requirements
This standard proposes specific normative requirements for wastewater, solid waste, exhaust gases, and noise generated during the enterprise's recycling process.
IV. Significance of Standard Implementation
According to data, China produced approximately 8.1 million tons of copper-based waste wires and cables and about 2 million tons of aluminum conductor-based waste wires and cables in 2021. Based on estimates, recycling and disassembling the aforementioned waste wires and cables could recover approximately 1.35 million tons of copper, 200,000 tons of aluminum, 1 million tons of steel, and about 7 million tons of polymer materials. While standardizing the recycling practices for waste wires and cables, this standard, by combining multiple sorting technologies and multi-stage sorting, ensures the maximization of renewable resource utilization, reducing the high mixing ratio of renewable resources caused by incomplete sorting, which adds unnecessary energy consumption for the users of these renewable resources, thereby contributing to China's energy conservation and emission reduction efforts. Furthermore, when enterprises conduct waste wire and cable recycling activities according to the requirements proposed in this standard, they have corresponding normative directions for rectifying the "three wastes" (waste water, gas, solid waste) and noise generated during the process. Building green and friendly enterprises can contribute to China's green environmental protection cause.
In summary, the revision of this standard has the following significant meanings: 1) It can improve the technical level of waste wire and cable recycling enterprises and reduce the industry's environmental pollution; 2) It further enhances the level of mechanization and automation of recycling operations, improving production efficiency and safety; 3) It promotes the development of enterprises towards larger scales, enhances the competitiveness of recycling enterprises, and encourages the healthy development of the industry; 4) It improves the efficiency of recycling and reusing various renewable resources, contributing to the national cause of renewable resource utilization.
Contact Information

